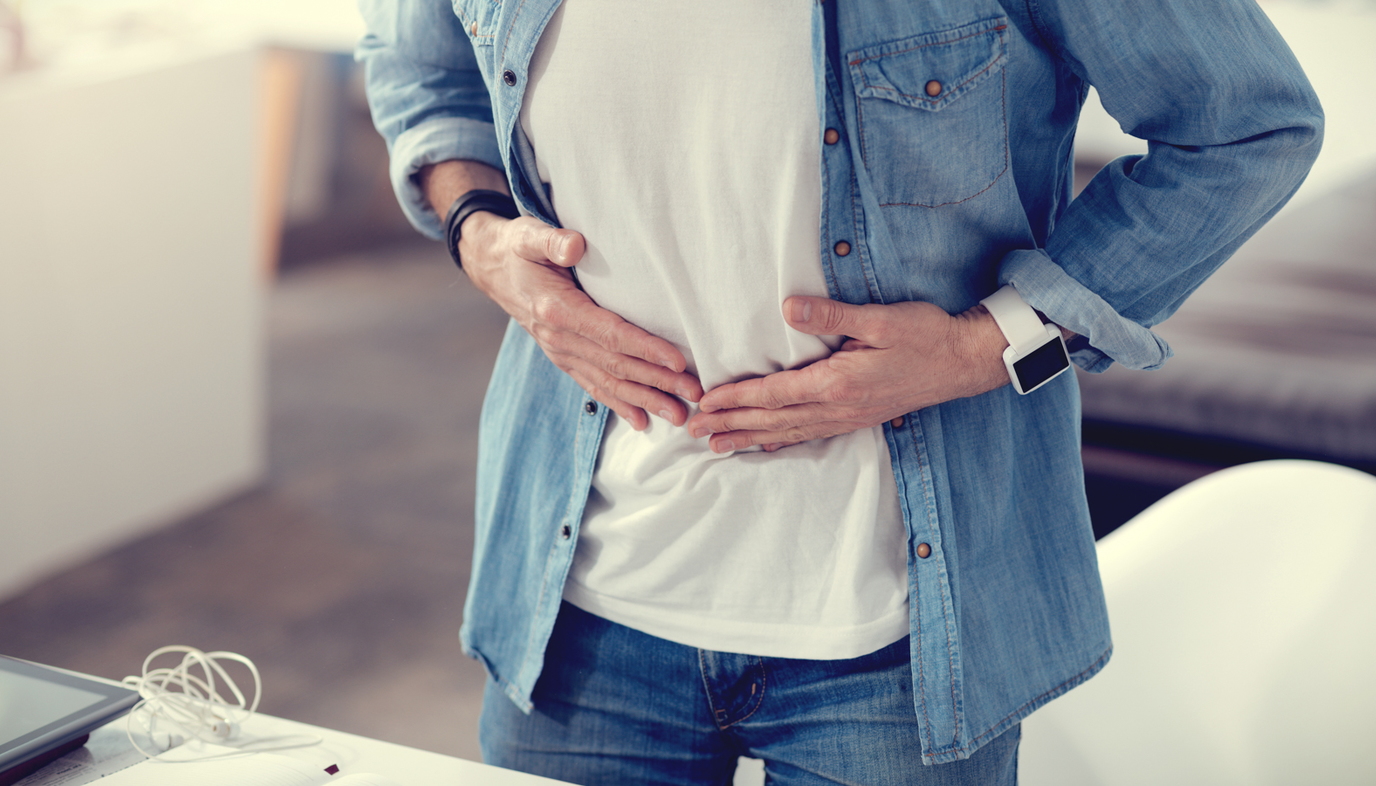

Attached to the first part of the colon, or cecum, is a worm-like projection otherwise known as your appendix. Its exact purpose is still not known, but we do now that we can live without it.
Research has indicated that perhaps the appendix is part of the body’s lymphatic system. Just like your lymph nodes swell when you’re sick and have an infection, so does your appendix. The latest findings also indicate that perhaps the appendix is our digestive system's good bacteria “safe haven.” Good bacteria that would normally be lost for whatever reason, seem to group up in the appendix, to be used when necessary. These good bacteria can soon turn bad when the appendix becomes blocked.
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix. The appendix can become blocked by feces that enter and have no way of exiting. Once the appendix becomes blocked, it begins to swell and become infected.
Surgical removal or appendectomy is generally the only method used in treating appendicitis due to the increased risk of the appendix rupturing. A ruptured appendix can lead to peritonitis (infection of the lining of the abdomen and abdominal organs) and abscess.
Appendicitis Is Considered a Medical Emergency
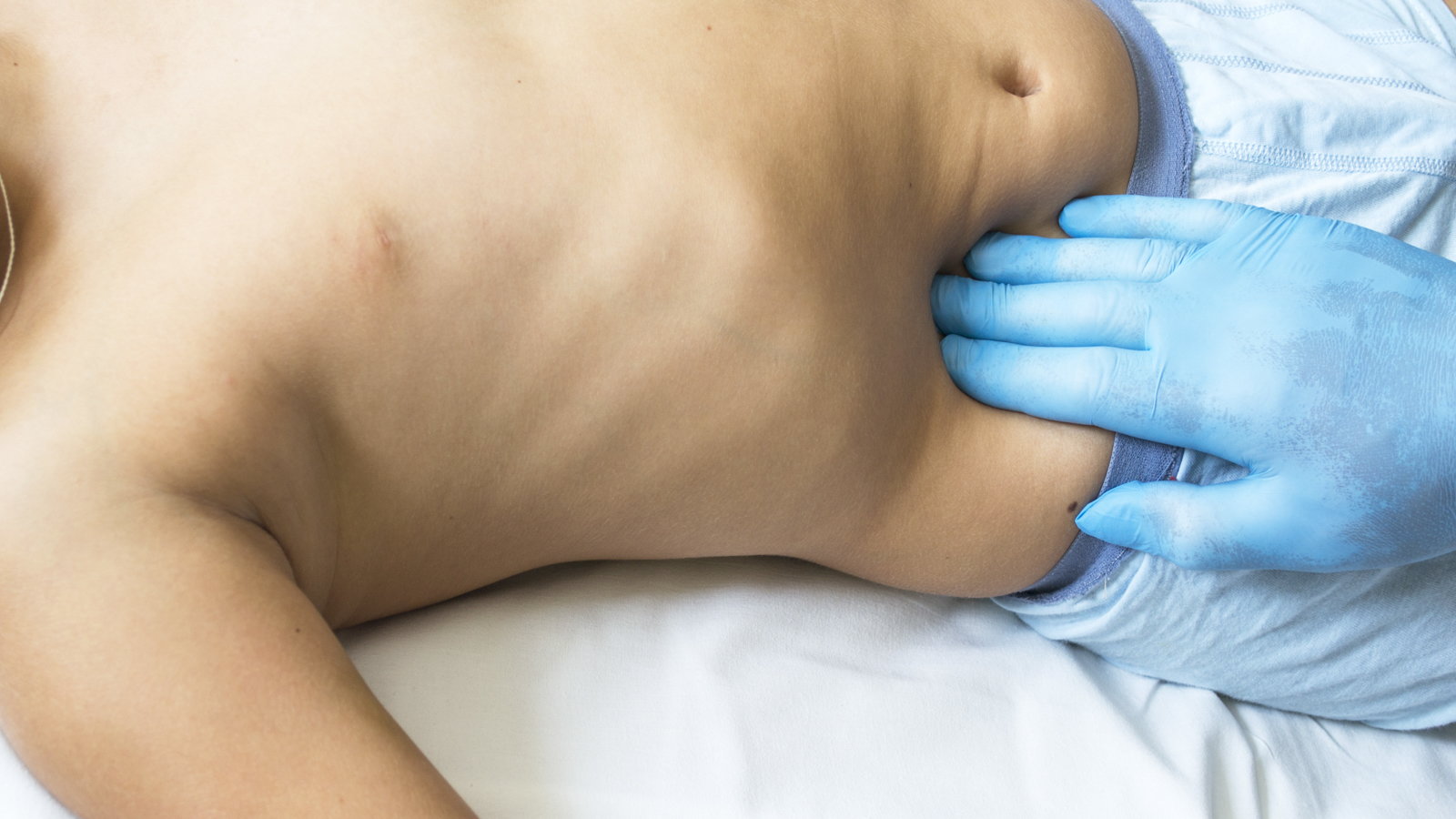
The first signs and symptoms of appendicitis is a dull achy pain around the navel that shifts to the lower right abdomen. As the infection increases, so does the pain. During an exam, when pressure is applied to the lower right portion of the abdomen, the area feels tender. When the pressure is removed, the pain severely increases. This is called rebound pain and is classic to appendicitis.
Other Appendicitis Symptoms Include:
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Constipation
- Abdominal swelling
- Fever
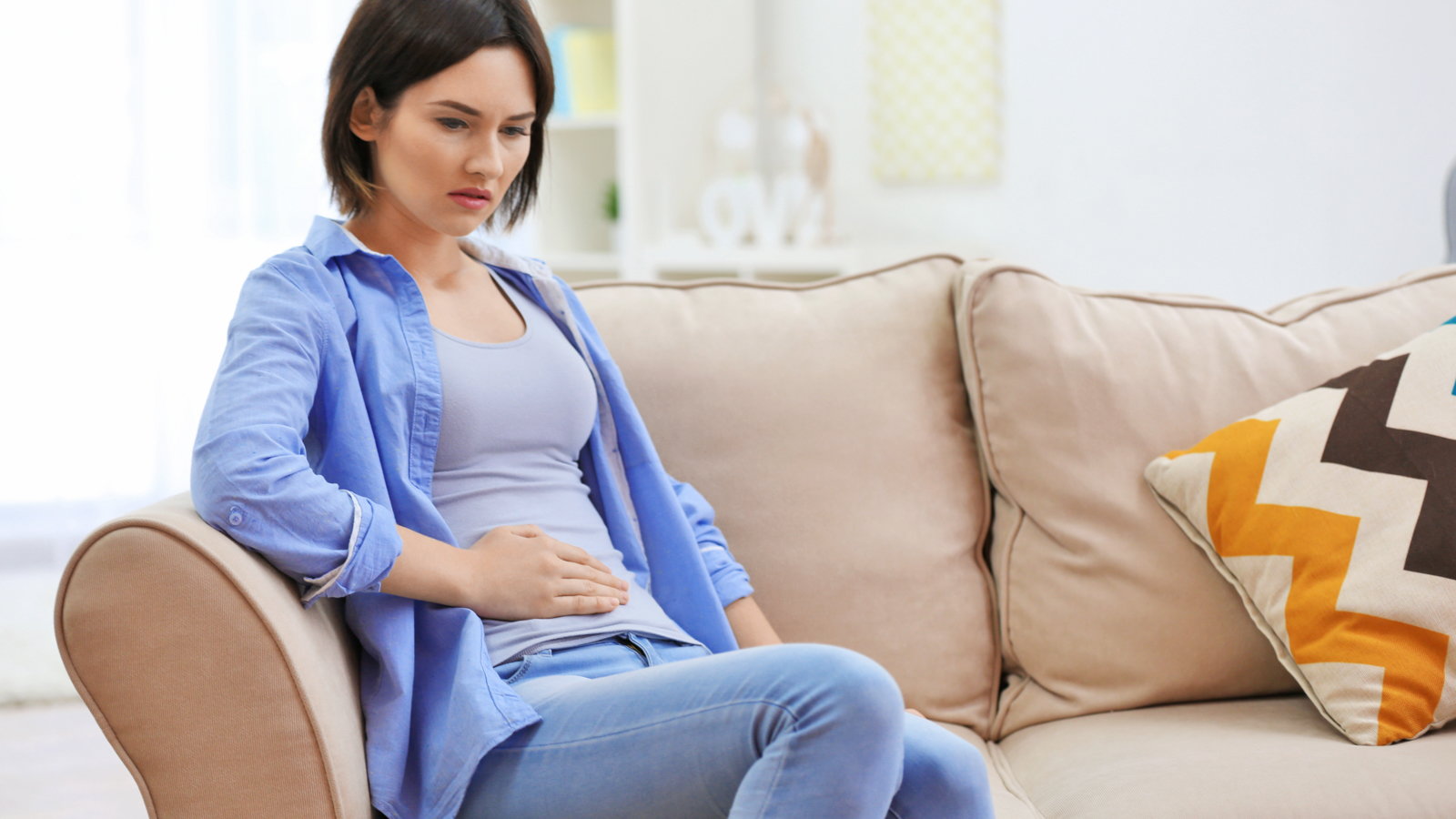

Children are much more likely to experience a ruptured appendix then an adult. If your child complains of a stomach ache, especially lower abdominal pain, do not delay in seeking medical treatment.
During an exam, a doctor may order several tests trying to make a diagnosis or rule out other conditions. Typically blood tests and a urine test will be ordered to check for elevated white blood cells.
Ultrasounds and CT scans are used to make a definitive diagnosis. A CT scan allows a doctor to better visualize internal organs.
Once a diagnosis is made, surgery will be performed. Doctors can choose to remove the appendix through open surgery, by making an incision into the abdomen, or by laparoscopic surgery.
Laparoscopic surgery involves the use of a laparoscope. A small incision is made into your abdomen so that the scope can fit and another small incision is made to fit small instruments to remove the appendix. After laparoscopic surgery is performed, several small “stab” holes will be present, instead of one long incision.
Recovery time is generally quicker and involves less scarring when the laparoscopic method is used.
Both methods require general anesthesia to be used.
Appendectomies are currently the most common abdominal surgery performed in the United States.
