Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a viral illness that occurs commonly in children, although it may be seen in adults as well. Hand, foot, and mouth disease is contagious, so children should be kept home from school or other group activities during the first few days of infection. Here are some valuable pieces of information to help you to avoid continuing the spread of the disease but also to help you understand the severity and symptoms.
Cause of Hand Foot and Mouth Disease:
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is caused by a group of viruses called enteroviruses. The most common enterovirus to cause hand, foot, and mouth disease is coxsackie virus A16. The virus is spread from direct person-to-person contact, not purely through being near a person with the disease. Secretions from the nose and throat, as well as contact with feces, are the most common ways of transmitting the infection. In general, hand, foot and mouth disease is not believed to be spread through airborne contact. Symptoms usually appear between 3-7 days of exposure.
Symptoms of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease:
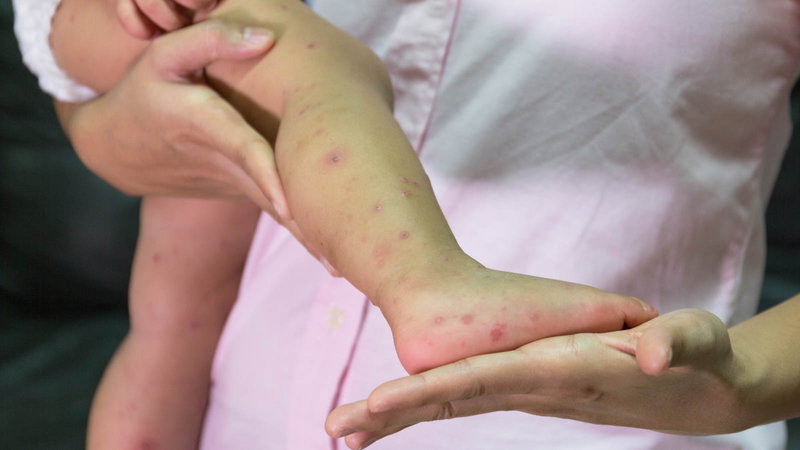
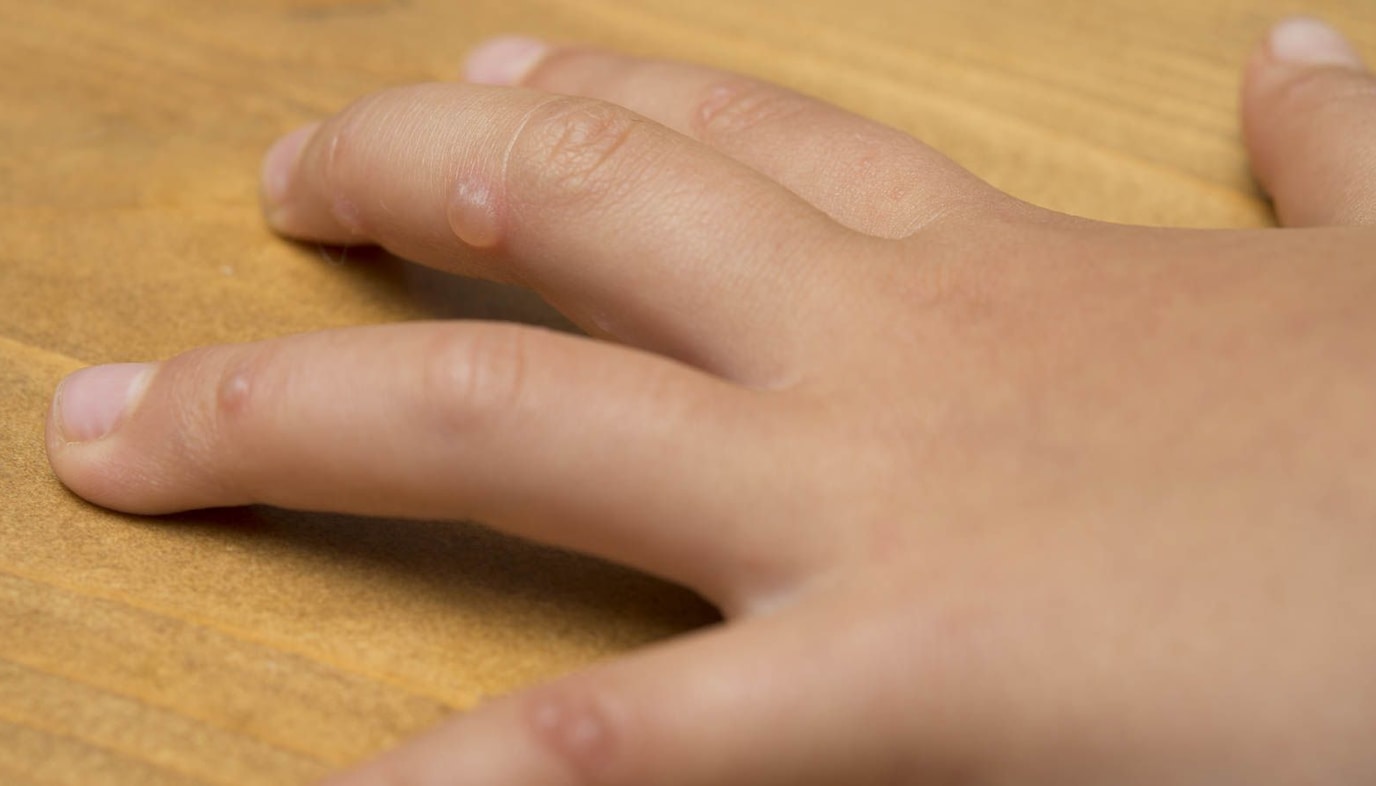
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is characterized by blisters of the hand, foot, and mouth. The blisters can be seen on the inside of the mouth, specifically on the cheeks, tongue, and gums. A skin rash may also occur. Blisters may be found on other parts of the body, including the diaper area. Fever is often present and is frequently the first symptom to appear. Other symptoms include lack of appetite, malaise, sore throat, cough, and occasionally diarrhea. Some of the symptoms are easy to mistake for flu-like symptoms, so pay attention to any and all symptoms that arise to help to differentiate between Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease and other illnesses.
Treatment of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease:
Since hand, foot, and mouth disease is a virus, there is no specific treatment available. Your doctor may recommend tylenol or motrin to help with the associated fever and pain. A mild local anesthetic, such as lidocaine, may be prescribed if blisters are particularly painful. Hand, foot, and mouth disease will usually run its course within 7-10 days.
Prevention of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease:
The number one way to prevent infection of hand, foot, and mouth disease or any viral infection is frequent hand washing. Children should be taught to wash their hands regularly particularly after using the bathroom and before meals. Caregivers should be careful to wash their hands after each and every diaper change. Children should be taught to cover their mouth and nose when they cough with a tissue if possible to reduce the amount of germs on their hands. If a tissue isn't available teach children to cover their mouth with their upper arm instead of their hands. Toys and other surfaces children come in contact with regularly should be cleaned with a disinfectant. Furthermore, if children begin exhibiting symptoms, do what is possible to keep them separate from other kids to slow the spread and avoid outbreaks in classrooms or daycare centers.